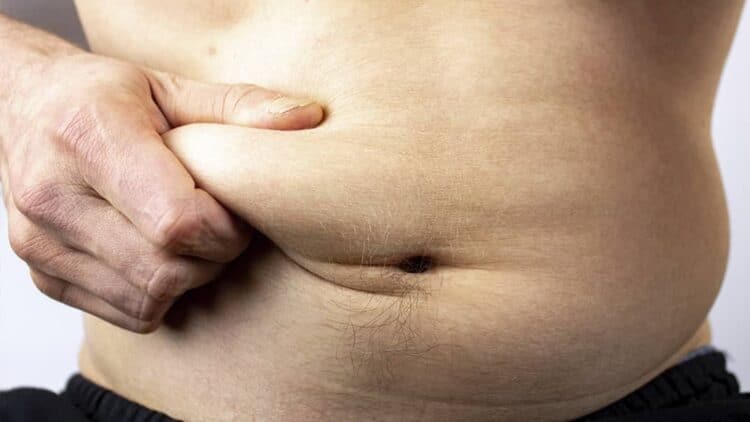
Eating quickly is not only a bad habit, but it is also linked to an increased risk of being overweight, abdominal obesity, and metabolic syndrome. According to the BBC, it takes between 5 and 20 minutes for the digestive system to send signals of satiety to the brain. The Center of Biomedical Research in Network explains that this leads to an intake of 100 or 200 additional calories per meal compared to those who eat more slowly. In addition, it also causes choices to lean more towards processed foods, with refined sugar or saturated fats, which cause an increase in blood sugar.
This in turn increases insulin release, which can lead to insulin resistance, causing fat to accumulate in the abdominal area. Eating more slowly allows the release of satiety hormones such as leptin and YY, reducing the desire to eat and thus controlling portion sizes.
Bad habit of eating quickly
Whether out of habit or due to the hectic pace of life we tend to lead today, many people eat extremely quickly without being aware of the risk this can pose to their health. It’s not just about inflammation, which leads to heavier digestion, but it can also contribute to increased abdominal fat.
According to the BBC, it takes between 5 and 20 minutes for the stomach’s signals of satiety to reach the brain. When we eat quickly, these signals arrive when we have already exceeded our calorie intake, consuming more than we should. According to the Center for Biomedical Research in Network, we can consume around 100 to 200 extra calories compared to people who eat more slowly.
Excessive quantities and sugar
In addition to excessive quantities, people who have this habit tend to gravitate toward more processed foods, with more white flour, saturated fats, and high levels of refined sugar. This is a problem because large amounts of sugar cause the release of insulin, and if this persists over time, it can lead to insulin resistance, which is related to the accumulation of fat in the abdominal area.
Benefits of eating slower
Experts undoubtedly consider that the best option is to take the time needed to eat, opting for a slower pace. In addition to promoting better digestion and reducing inflammation, it also affects metabolism and appetite. At the same time, it releases satiety hormones such as leptin and ghrelin, which are responsible for reducing the urge to continue eating, helping to control portion sizes. In addition to eating slowly, experts also recommend chewing each bite calmly, chewing between 20 and 30 times.
It is also important to put down your cutlery between bites and not use your cell phone or watch television while eating. Drinking water before and during meals also helps you feel fuller. In addition to correcting eating habits (if necessary), it is important to maintain an active lifestyle, avoiding a sedentary lifestyle. Commit to a balanced diet, good habits, physical activity, and good sleep hygiene.